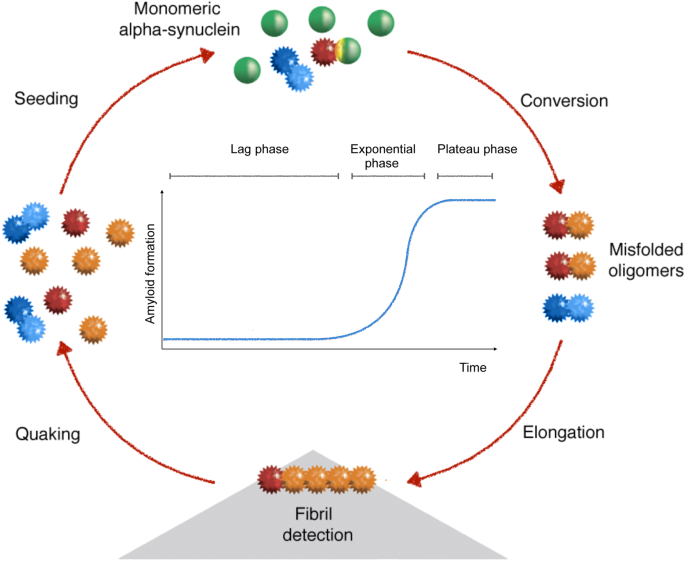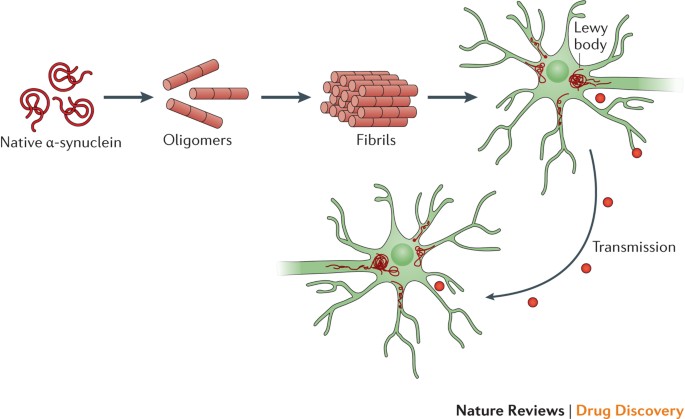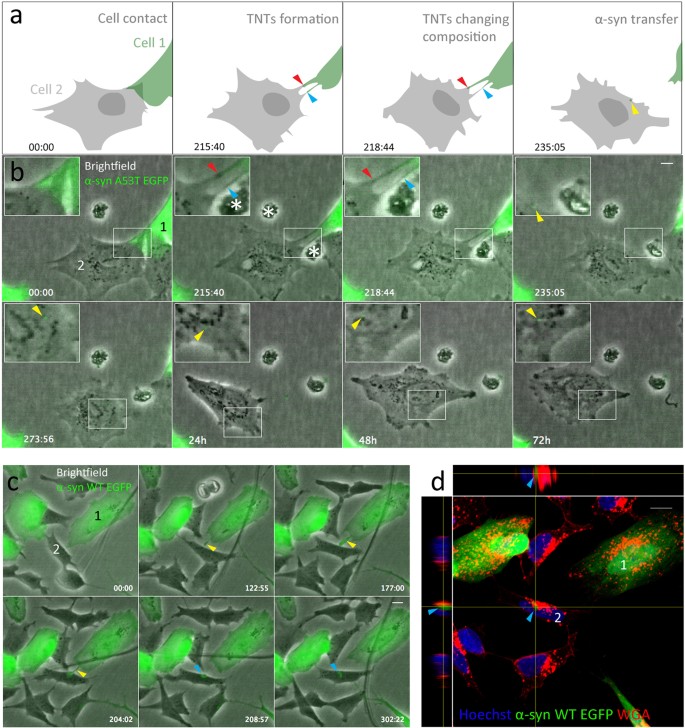
α-synuclein transfer through tunneling nanotubes occurs in SH-SY5Y cells and primary brain pericytes from Parkinson's disease patients | Scientific Reports
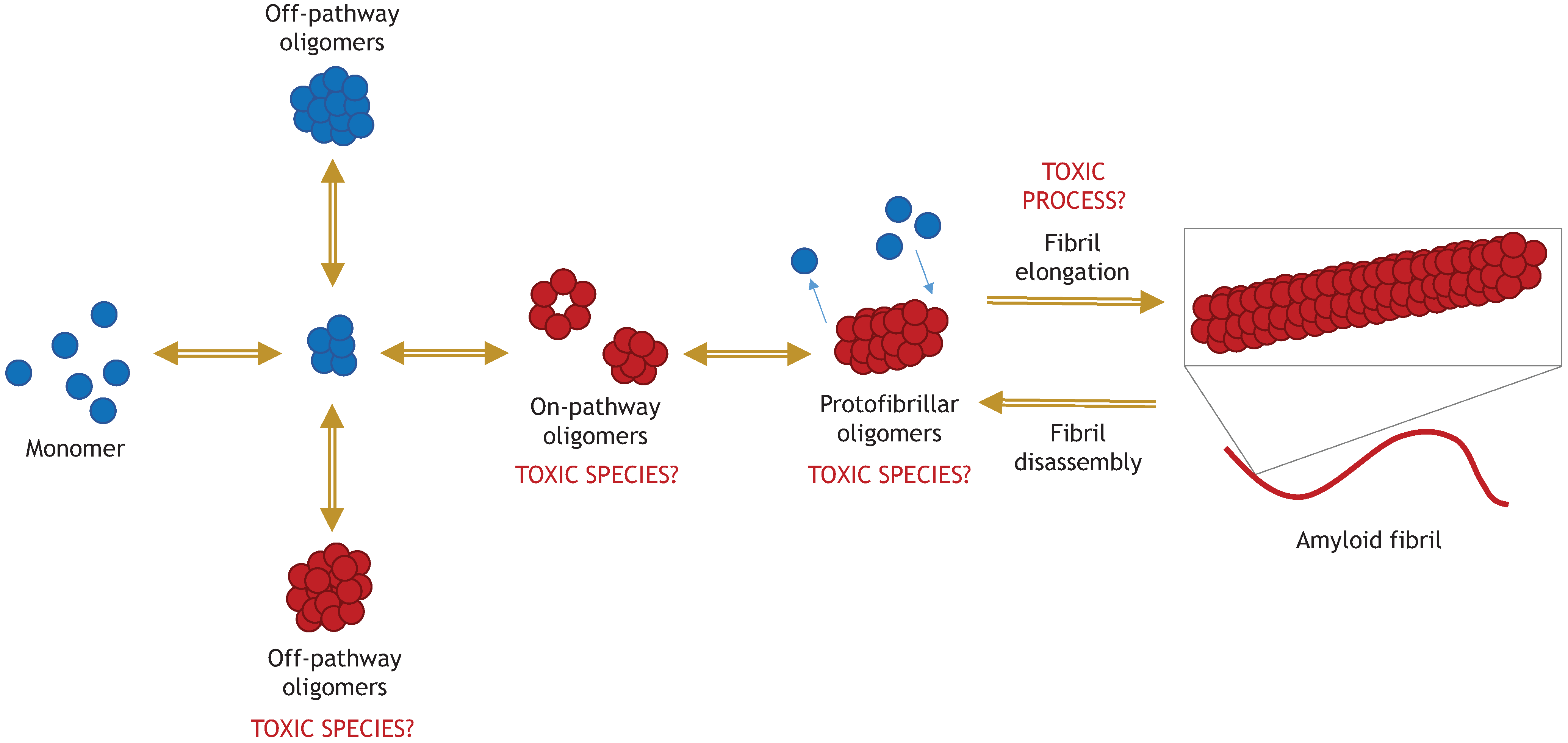
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Seeking a Mechanism for the Toxicity of Oligomeric α-Synuclein | HTML

Subcellular localization of alpha-synuclein aggregates and their interaction with membranes Miraglia F, Ricci A, Rota L, Colla E - Neural Regen Res

A role for α-Synuclein in axon growth and its implications in corticostriatal glutamatergic plasticity in Parkinson's disease | Molecular Neurodegeneration | Full Text
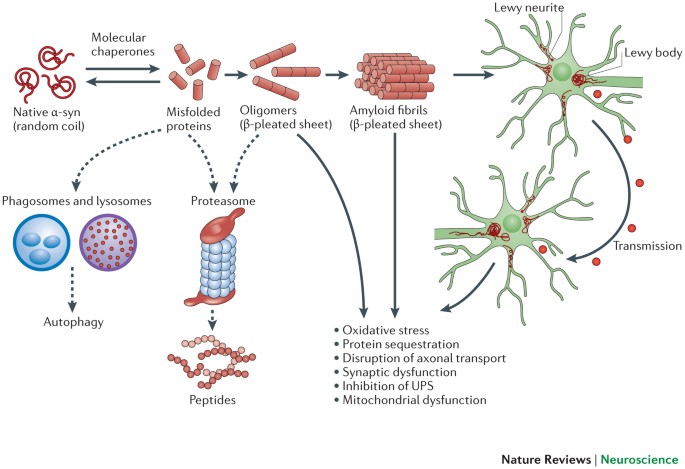
Parkinson's disease dementia: convergence of α-synuclein, tau and amyloid-β pathologies | Nature Reviews Neuroscience
Single-Channel Electrophysiology Reveals a Distinct and Uniform Pore Complex Formed by α-Synuclein Oligomers in Lipid Membranes
Single-Channel Electrophysiology Reveals a Distinct and Uniform Pore Complex Formed by α-Synuclein Oligomers in Lipid Membranes

α-Synuclein oligomers mediate the aberrant form of spike-induced calcium release from IP 3 receptor | Scientific Reports

The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target | Nature Reviews Neuroscience
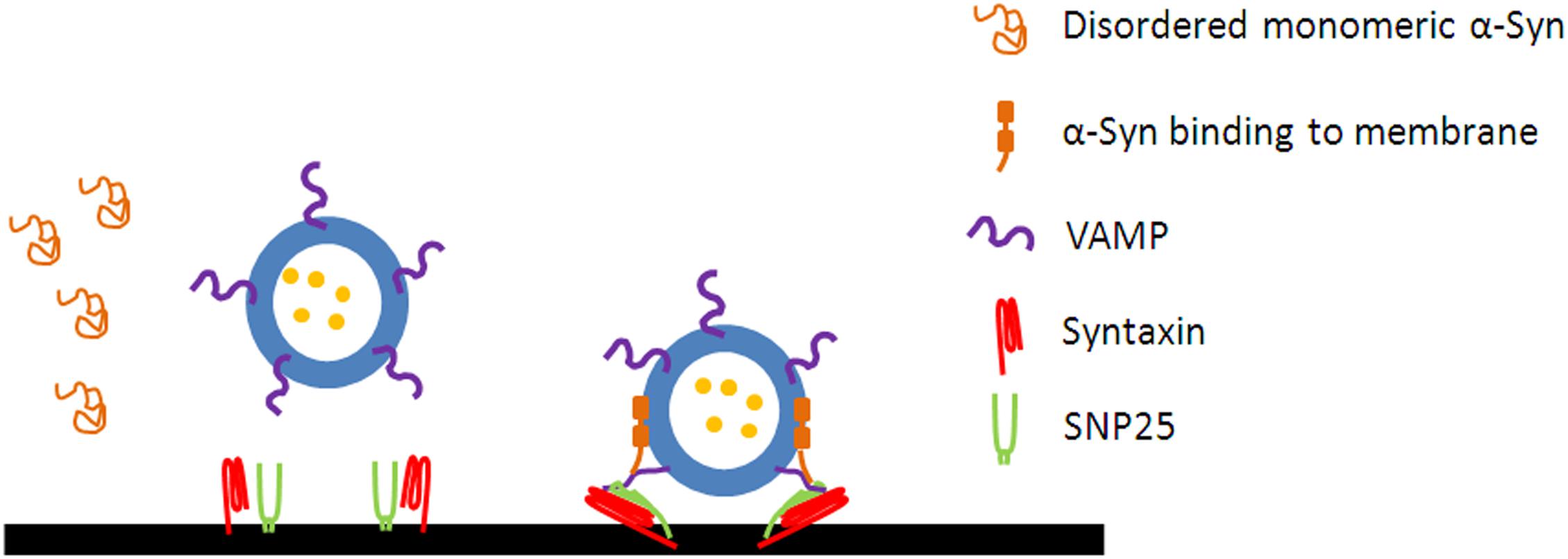
Frontiers | α-Synuclein: A Multifunctional Player in Exocytosis, Endocytosis, and Vesicle Recycling | Neuroscience
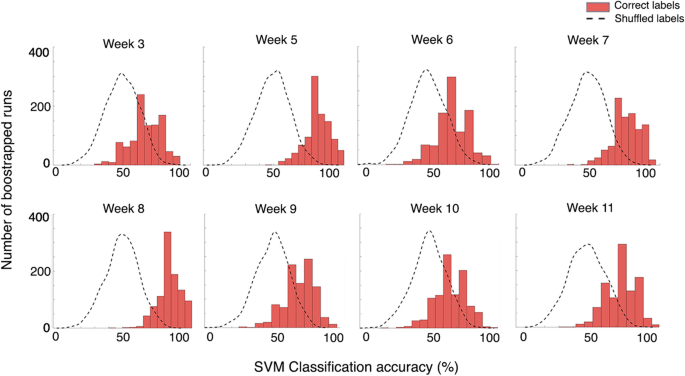
Classification of α-synuclein-induced changes in the AAV α-synuclein rat model of Parkinson's disease using electrophysiological measurements of visual processing | Scientific Reports
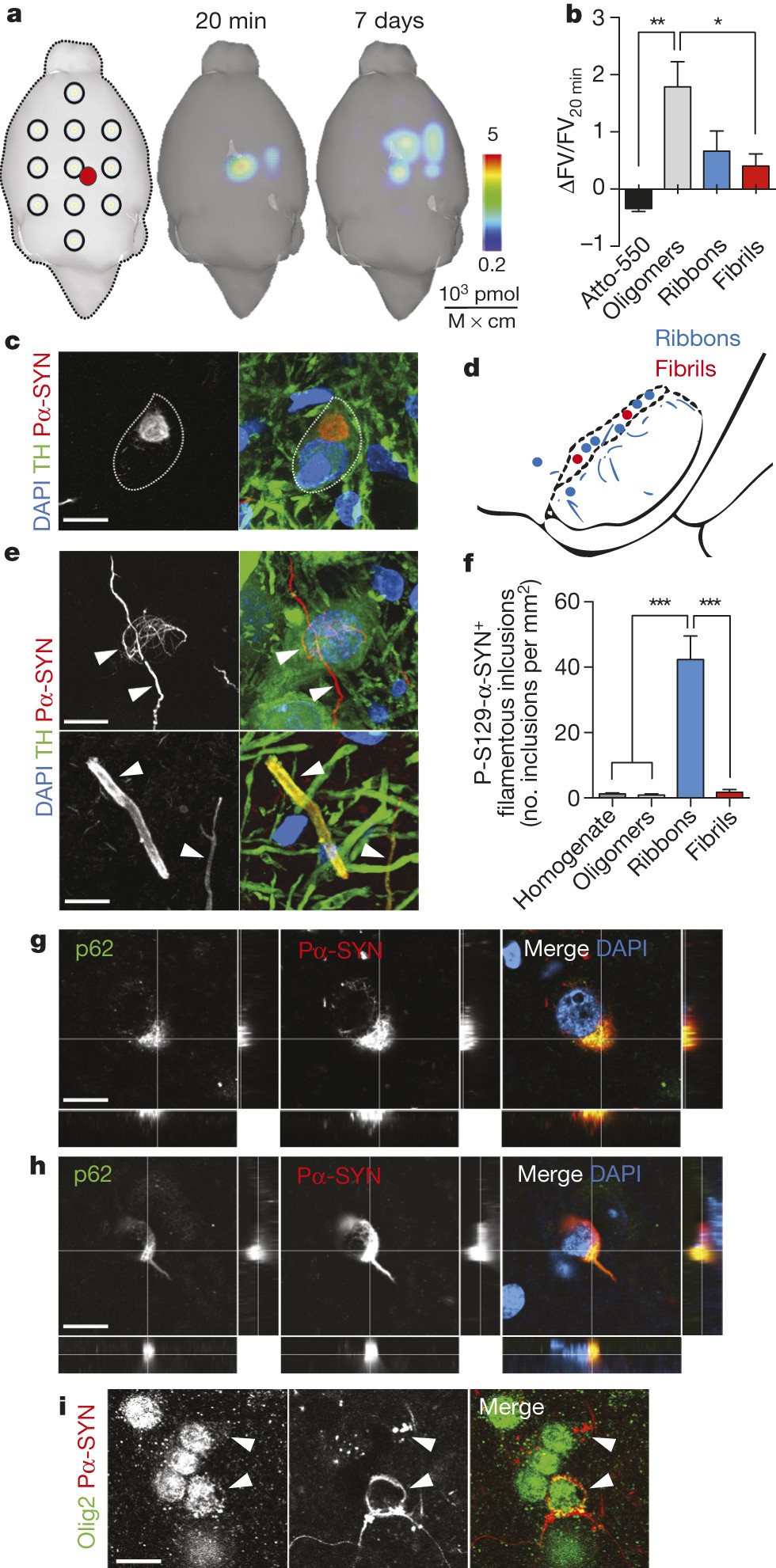
α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration | Nature
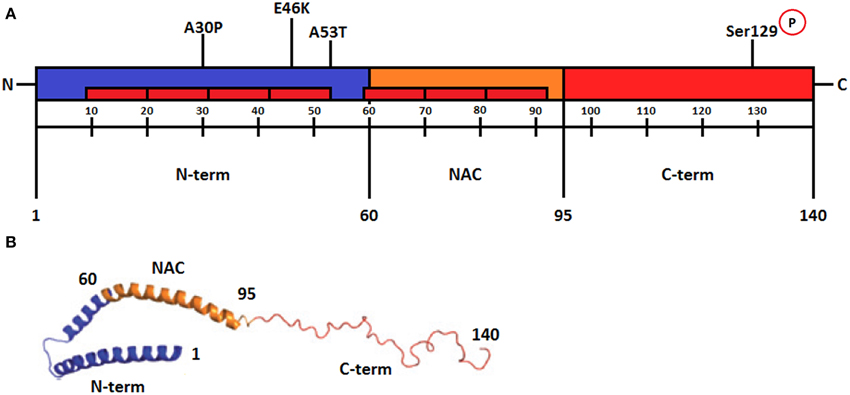
Frontiers | Features of alpha-synuclein that could explain the progression and irreversibility of Parkinson's disease | Neuroscience
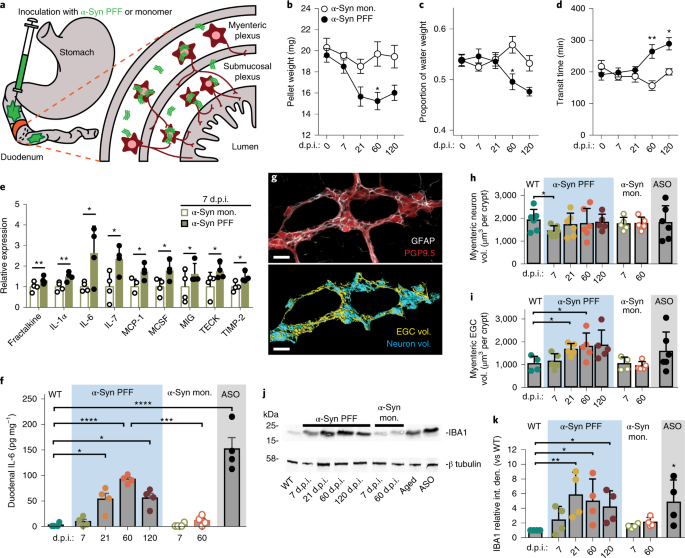
Gut-seeded α-synuclein fibrils promote gut dysfunction and brain pathology specifically in aged mice | Nature Neuroscience
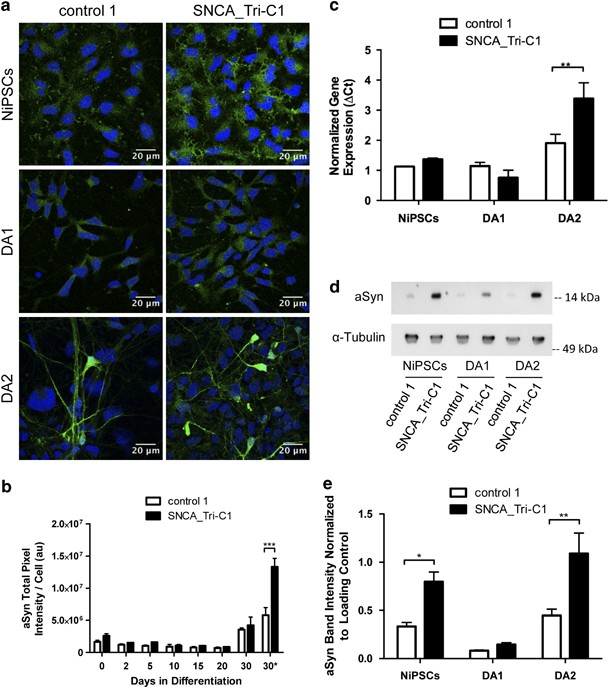
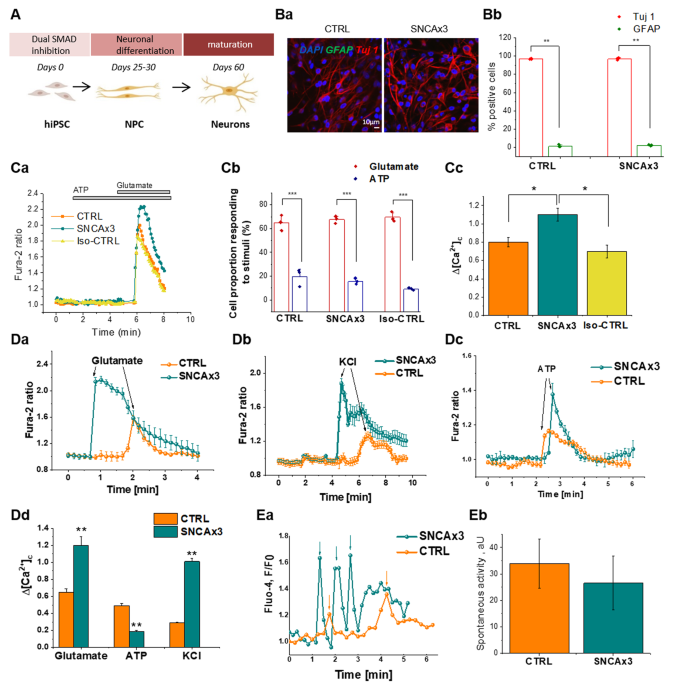
Elevated α -synuclein caused by SNCA gene triplication impairs neuronal differentiation and maturation in Parkinson's patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells | Cell Death & Disease

Early synaptic dysfunction induced by α-synuclein in a rat model of Parkinson's disease | Scientific Reports
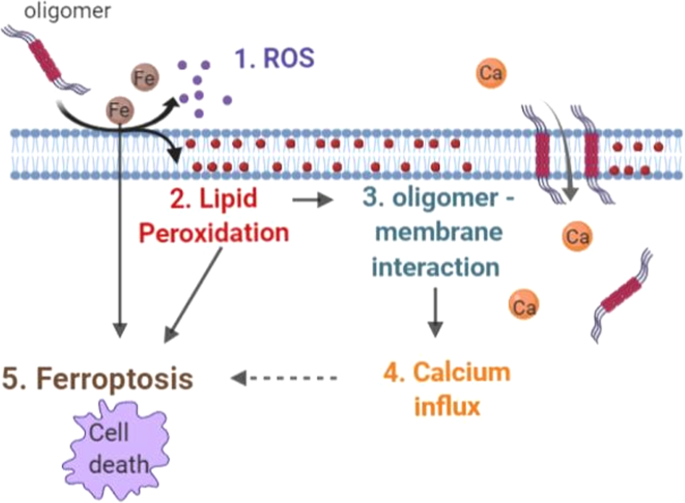
Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: an interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidation | Cell Death & Differentiation

CD spectra of α-synuclein species incubated with vesicles of different... | Download Scientific Diagram
Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: an interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidation | Cell Death & Differentiation

Seeding and transgenic overexpression of alpha‐synuclein triggers dendritic spine pathology in the neocortex | EMBO Molecular Medicine